- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping

Product
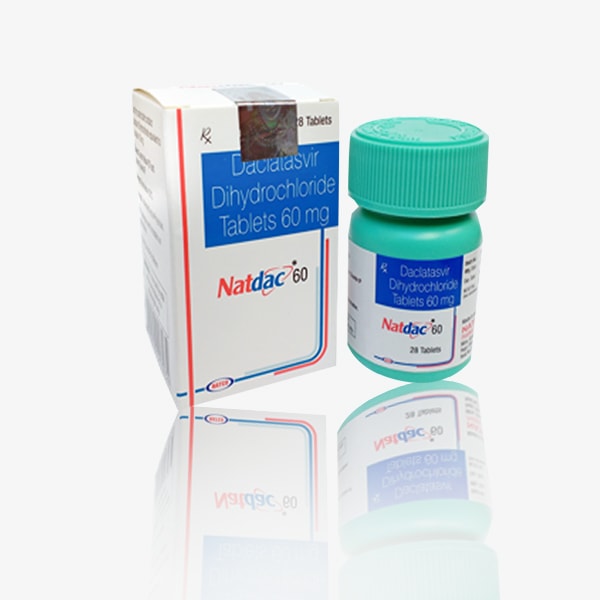
Introduction: Natdac, featuring Daclatasvir as its active ingredient, represents a significant advancement in the management of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. This comprehensive overview navigates through the history, mechanism of action, therapeutic applications, administration, potential side effects, and considerations associated with Natdac Daclatasvir.
I. History: Daclatasvir, discovered and developed in the early 21st century, marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of HCV infection. Its approval for medical use, including formulations like Natdac, has transformed the landscape of hepatitis C therapy, offering hope to millions of individuals worldwide.
II. Mechanism of Action: Daclatasvir is a potent inhibitor of the NS5A protein, a key component in the replication of the hepatitis C virus. By targeting NS5A, Daclatasvir disrupts viral replication and assembly, ultimately leading to the suppression of HCV infection within the body.
III. Therapeutic Applications: Natdac Daclatasvir is employed in the treatment of:
- Chronic Hepatitis C Infection: It is indicated for the treatment of chronic HCV infection, encompassing various genotypes and patient populations.
- Cirrhosis: Daclatasvir is also utilized in individuals with compensated cirrhosis due to HCV infection, helping to prevent disease progression and liver-related complications.
IV. Administration and Dosage: Natdac Daclatasvir is typically administered orally in tablet form. The recommended dosage and duration of treatment may vary depending on factors such as HCV genotype, prior treatment history, and the presence of liver cirrhosis. Treatment regimens often involve combination therapy with other direct-acting antiviral agents.
V. Potential Side Effects: While generally well-tolerated, Natdac Daclatasvir may cause side effects, including:
- Fatigue: Some individuals may experience fatigue or weakness during treatment.
- Headache: Mild to moderate headaches may occur but are usually transient.
- Nausea and Diarrhea: Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea may be observed.
VI. Considerations and Monitoring:
- Liver Function Monitoring: Regular monitoring of liver function is essential throughout treatment to assess treatment response and detect any signs of liver-related complications.
- Drug Interactions: Daclatasvir may interact with certain medications, including antiretroviral drugs and some statins. Close monitoring and dose adjustments may be necessary when co-administering medications.
VII. Conclusion: Natdac Daclatasvir stands as a pivotal component in the comprehensive management of chronic hepatitis C infection. Its potent antiviral activity, coupled with its favorable safety profile, has positioned it as a cornerstone in HCV therapy, offering renewed hope for individuals affected by this challenging condition. As research continues to advance, Natdac remains at the forefront of efforts to combat hepatitis C, paving the way for improved outcomes and quality of life for patients worldwide.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.