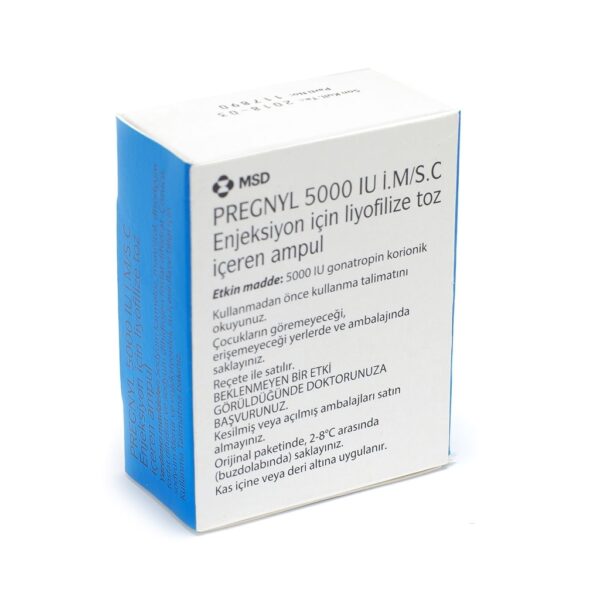

Buy PREGNYL 5000IU HCG Online
$28.60
CHARACTERISTICS
DOSAGE 500-3000IU 1-3 TIMES/WEEK
ACTIVE SUBSTANCE HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN
FORM 1 AMP X 5000 IU
MANUFACTURER ORGANON

Buy PREGNYL 5000IU HCG Online
$28.60
- Description
- Reviews (0)
Description
Formula: C1105H1770N318O336S26
Introduction
Pregnyl, containing Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) as its active ingredient, serves as a vital medication in reproductive medicine. Designed to mimic the action of luteinizing hormone (LH), Pregnyl plays a crucial role in stimulating ovulation and supporting fertility in both men and women. This description aims to provide insights into the characteristics, clinical applications, and considerations associated with Pregnyl (HCG).
Mechanism of Action
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy, primarily by the placenta. In reproductive medicine, HCG acts similarly to luteinizing hormone (LH), which triggers the release of eggs from the ovaries in women and stimulates the production of testosterone in men. By mimicking LH, Pregnyl helps regulate ovulation in women and supports the production of sperm in men.
Clinical Applications
- Ovulation Induction: Pregnyl is commonly used in women undergoing fertility treatment to induce ovulation. It is often administered in conjunction with other medications, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), to stimulate the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles.
- Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART): Pregnyl is a crucial component of various assisted reproductive techniques, including in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). It helps trigger the final maturation of eggs before they are retrieved for fertilization.
- Treatment of Hypogonadism: In men with hypogonadism (low testosterone levels), Pregnyl may be used to stimulate the production of testosterone, thereby improving fertility and overall reproductive health.
Dosage Forms and Administration
Pregnyl is typically available in the form of a powder for injection, which is reconstituted with a solvent before administration. The dosage and administration regimen vary depending on the specific indication and the individual patient’s response to treatment. It is usually administered by healthcare professionals through intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
Characteristics and Considerations
- Timing of Administration: The timing of Pregnyl administration is critical, particularly in fertility treatment cycles. It is usually given when the ovarian follicles are adequately developed, as determined by ultrasound monitoring.
- Ovulation Monitoring: Close monitoring of ovulation is essential during Pregnyl therapy to ensure optimal timing for intercourse or assisted reproductive procedures. Ultrasound monitoring and hormone level assessments help assess follicular growth and predict ovulation.
- Multiple Gestation Risk: Pregnyl therapy may increase the risk of multiple gestations (twins, triplets, etc.) due to the stimulation of multiple follicles. Healthcare providers carefully monitor treatment to minimize this risk and ensure the safety of both the mother and babies.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): In some cases, Pregnyl therapy may lead to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, characterized by enlarged ovaries and fluid accumulation in the abdomen. Close monitoring and early intervention help mitigate this risk.
- Side Effects: Common side effects of Pregnyl may include injection site reactions, abdominal discomfort, breast tenderness, and mood swings. These side effects are generally mild and transient.
Conclusion
Pregnyl, containing Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), plays a pivotal role in supporting fertility and reproductive health in both men and women. Its ability to mimic the action of luteinizing hormone (LH) makes it a valuable tool in ovulation induction and assisted reproductive techniques. As with any medication in reproductive medicine, the use of Pregnyl involves careful monitoring and individualized treatment plans tailored to the specific needs of each patient. Through its contributions to fertility treatment, Pregnyl offers hope and support to individuals and couples on their journey toward building a family.
Be the first to review “Buy PREGNYL 5000IU HCG Online” Cancel reply
Related Products
Buy CHORIOMON (HCG) 5000IU Online
Total Sales: 0
SKU: 491875





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.