- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping

Product
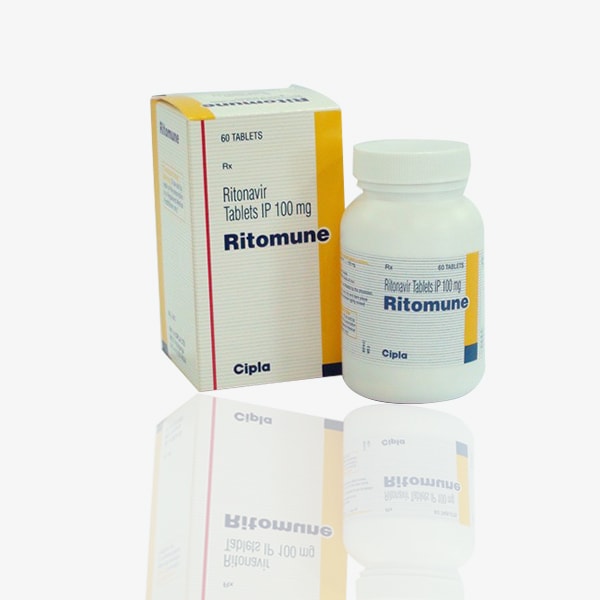
Ritomune is a medication that contains the active ingredient ritonavir. It is a type of medication known as a protease inhibitor and is primarily used in the treatment of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection. Below is a general description:
Ritonavir (Ritomune):
Indications:
- HIV Infection: Ritomune is indicated for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in combination with other antiretroviral medications. It helps to reduce the viral load and slow down the progression of HIV disease.
Mechanism of Action:
- Ritomune works by inhibiting the activity of the HIV protease enzyme. This enzyme is necessary for the replication of the HIV virus. By inhibiting protease, ritonavir prevents the virus from maturing and producing infectious viral particles.
Combination Therapy:
- Ritomune is typically used as part of a combination regimen of antiretroviral medications. Combining multiple drugs with different mechanisms of action helps to suppress HIV replication more effectively and reduce the risk of drug resistance.
Administration:
- Ritomune is usually taken orally in the form of tablets. The dosage and frequency of administration may vary based on individual patient factors and response to treatment.
Dosage:
- The recommended dosage of Ritomune for the treatment of HIV infection is typically 100 mg twice daily or as directed by a healthcare provider. The dosage may be adjusted based on individual patient factors, such as tolerance to side effects and interactions with other medications.
Duration of Treatment:
- Treatment with Ritomune is usually long-term and may be continued indefinitely as part of a maintenance therapy regimen for HIV infection.
Monitoring:
- Patients receiving Ritomune may undergo regular medical evaluations, including blood tests to monitor viral load, CD4 cell count, and liver function, to assess treatment response and manage potential side effects.
Side Effects:
- Common side effects of Ritomune may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, and fatigue. Serious side effects, although less common, may include liver toxicity, pancreatitis, and changes in heart rhythm.
Contraindications and Precautions:
- Ritomune may be contraindicated in individuals with a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to ritonavir or any of its components. It should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing liver or heart conditions.
Patient Counseling:
- Patients prescribed Ritomune should be educated about potential side effects, the importance of adhering to the treatment plan, and the need for regular medical monitoring.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
- The use of Ritomune during pregnancy is generally not recommended unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Women of childbearing age should use effective contraception during Ritomune therapy. It is not known whether Ritomune passes into breast milk, so breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment.
It’s important to note that specific details about the use of Ritomune should be discussed with a healthcare professional. The medication should be used under the guidance and supervision of a qualified healthcare provider based on the individual’s medical history and specific health needs.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.